Description
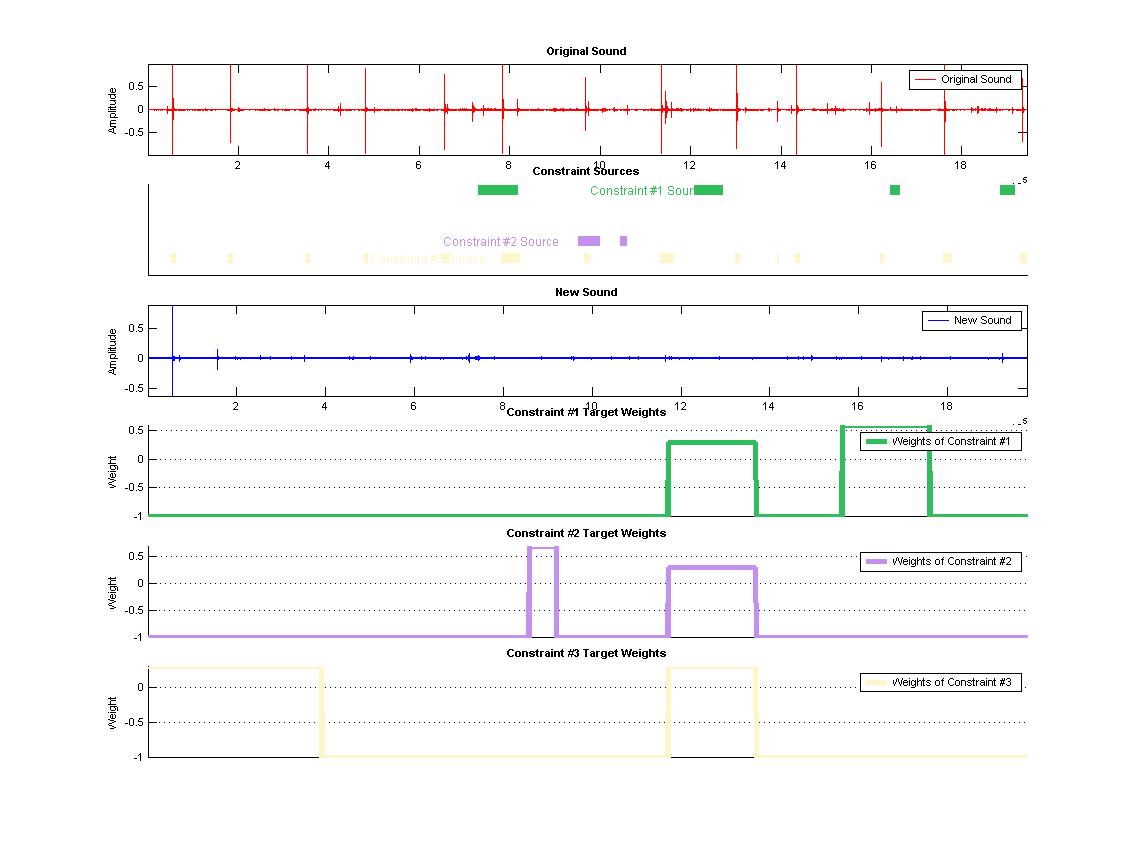
Input Sound
Baseball practice sounds.
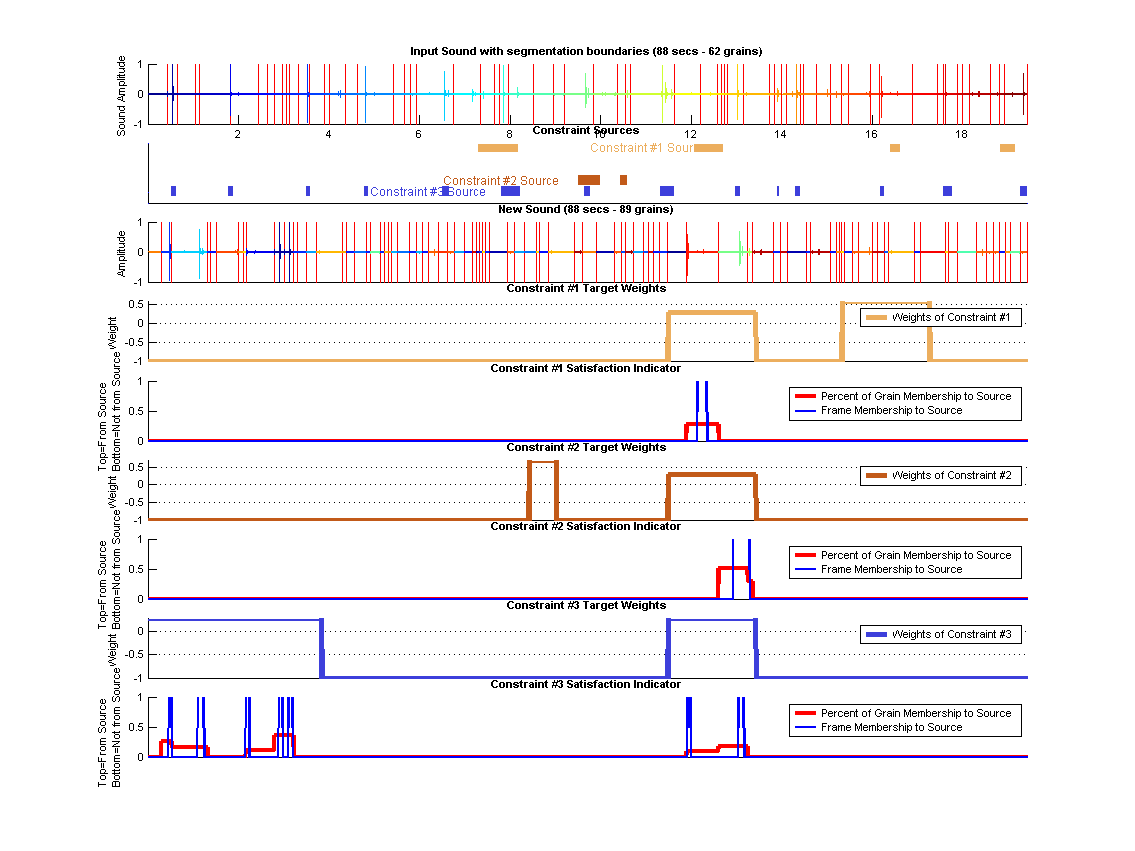
Synthesis Constraints
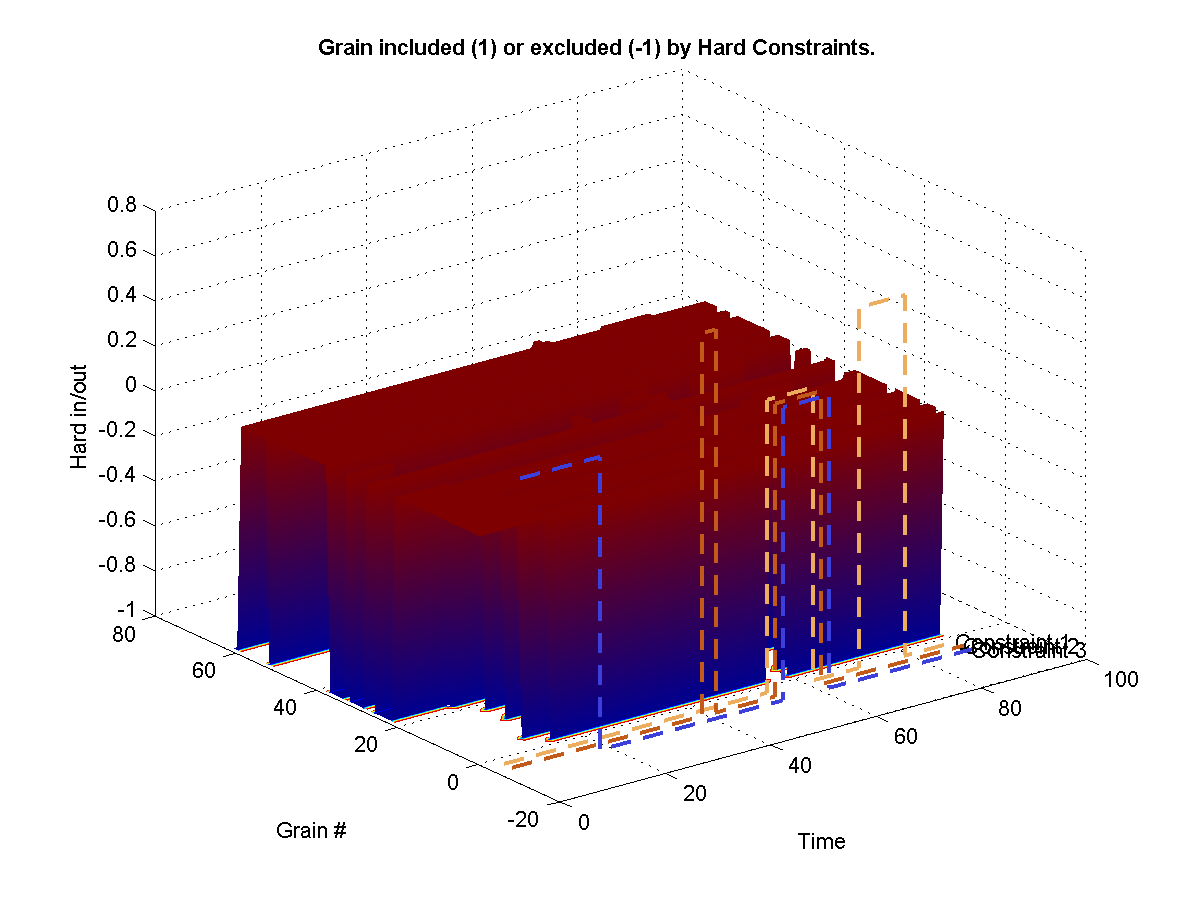
| Source 1 | 4 source segments consisting of a spectator laughing sounds.
|
| Target 1 | Hard -1 exclusion constraint most of the time, low weight soft weights for some periods.
|
| Source 2 | 2 source segments consisting of a spectator calling ball.
|
| Target 2 | Hard -1 exclusion constraint most of the time, low weight soft weights for some periods.
|
| Source 3 | Many source segments consisting of a loud ball hitting sounds.
|
| Target 3 | Hard -1 exclusion constraint most of the time, low weight soft weights for some periods.
|
Comments
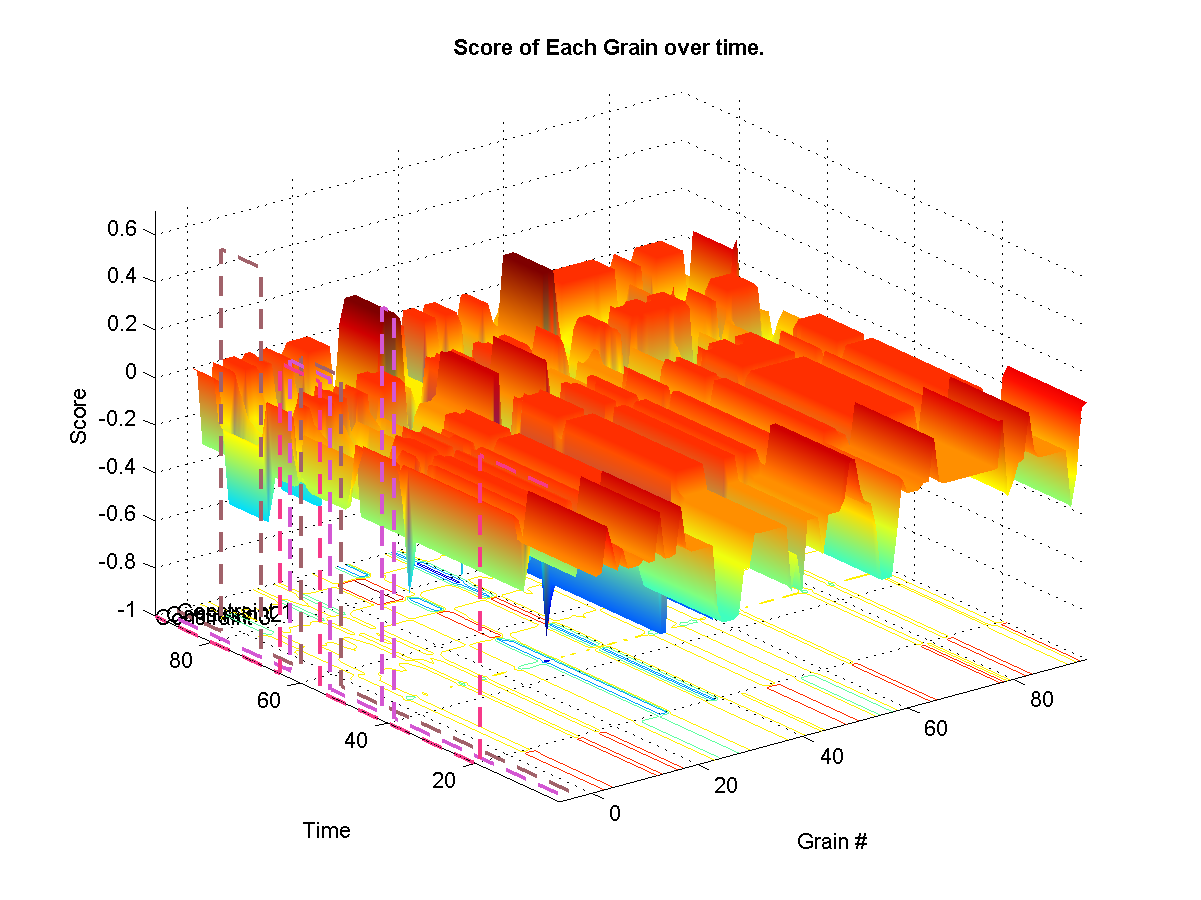
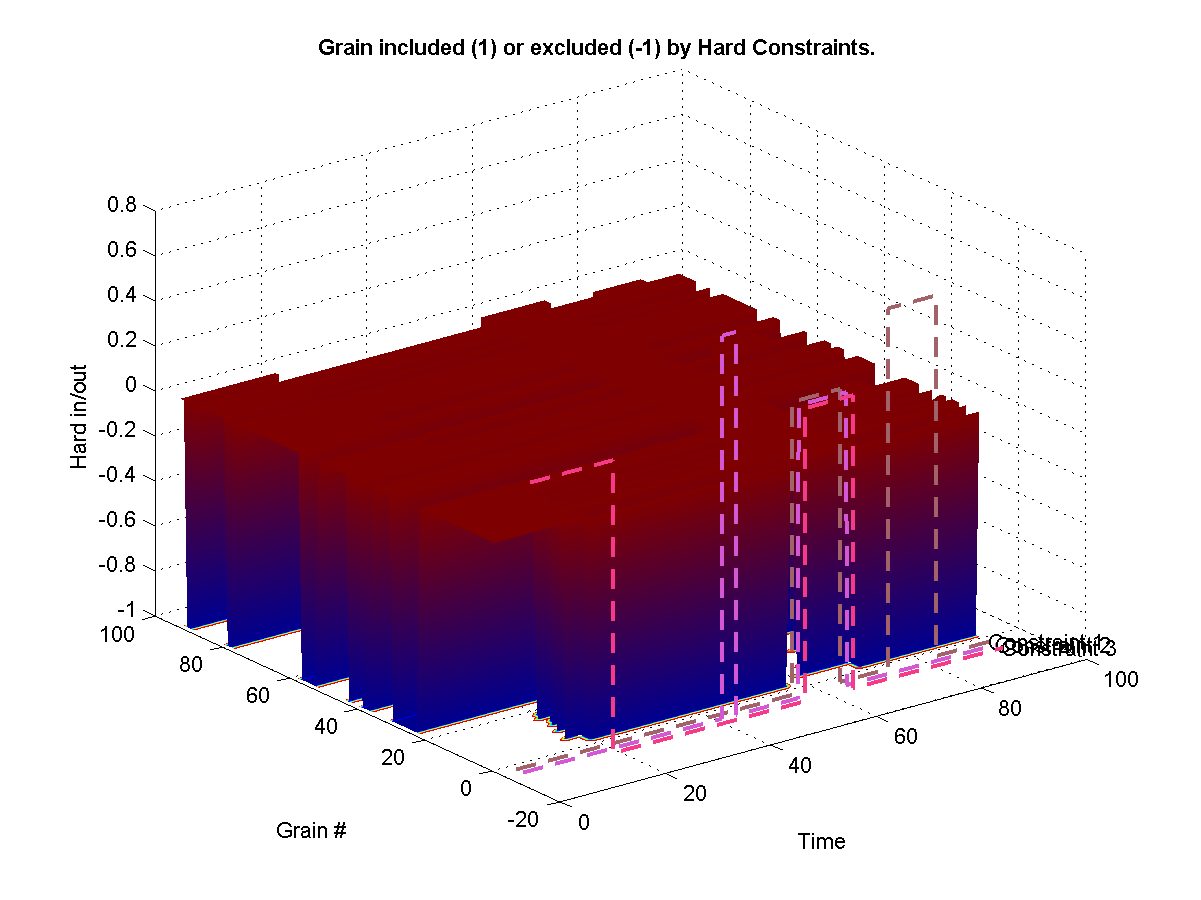
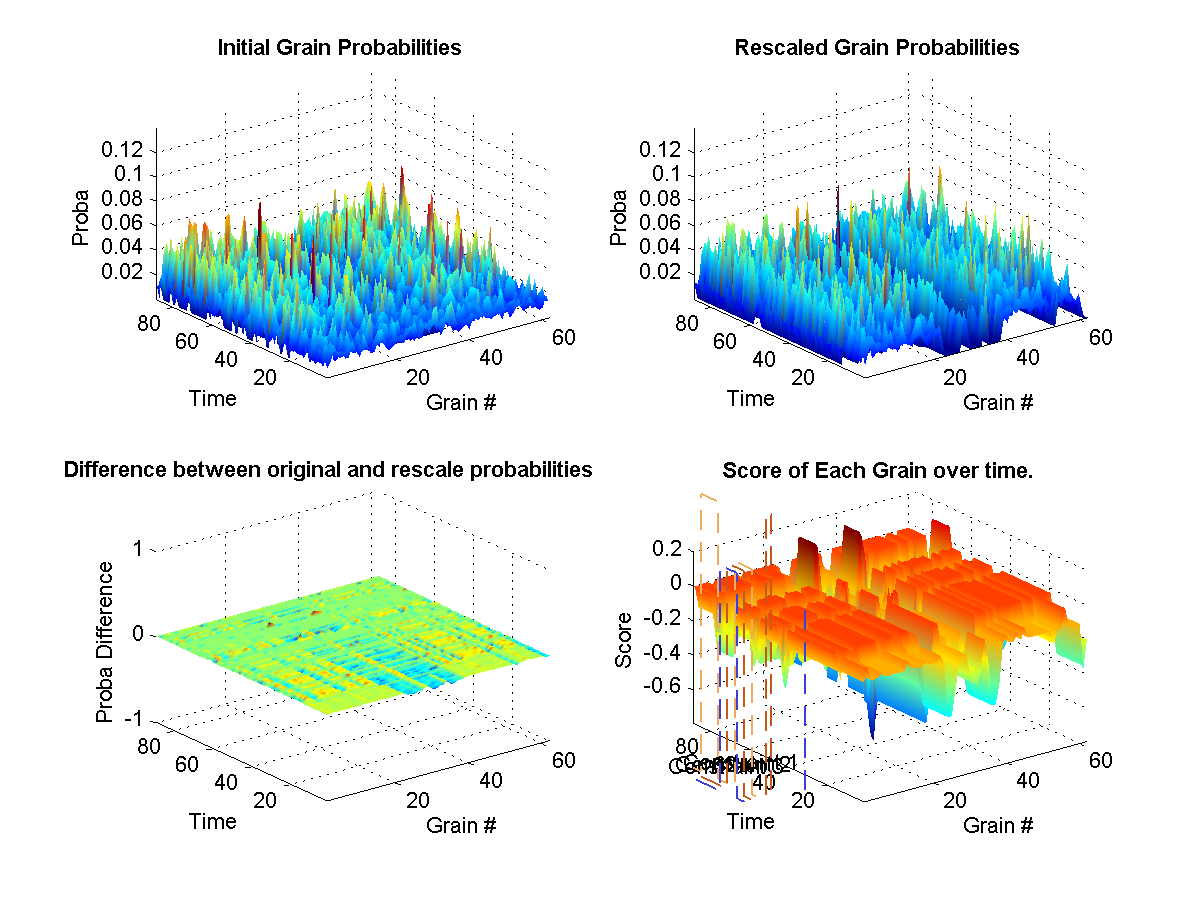
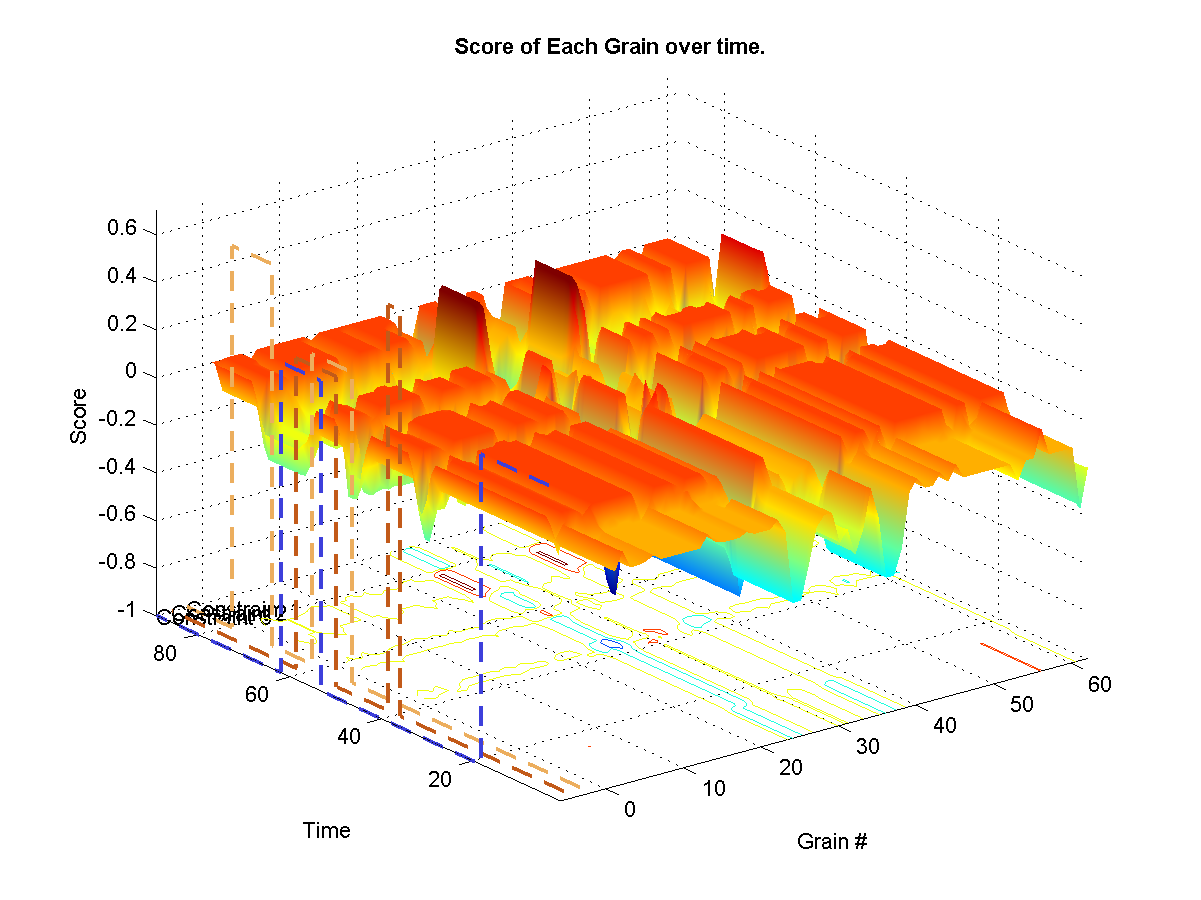
Uses a hard exclusion sounds during most periods and introduces source sounds at given intervals. We only use very light weights so that sources are introduced slightly more frequently than unconstrained synthesis. Notice overlapping source as well as targets.
|
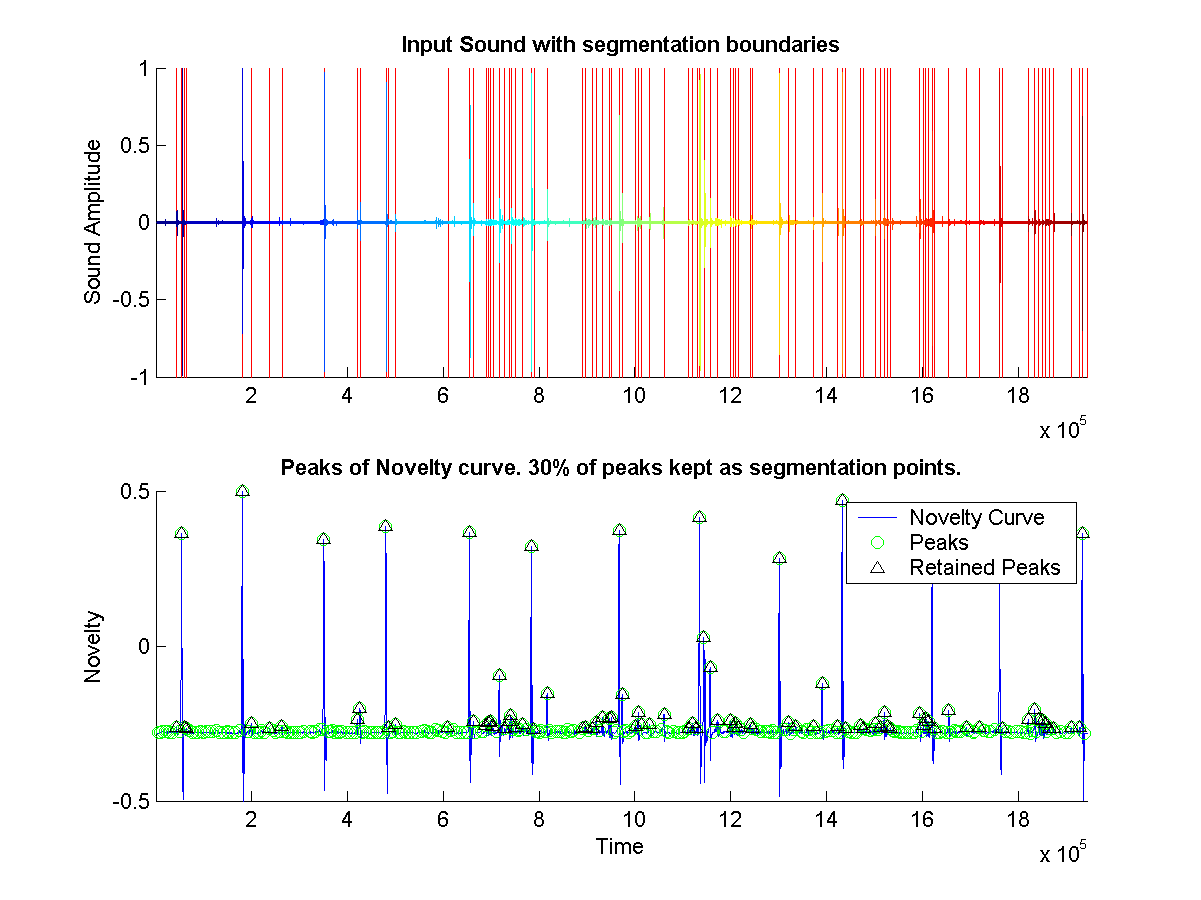
Self-Similarity Synthesis
|
Segmented Original Sound

New Sound
|
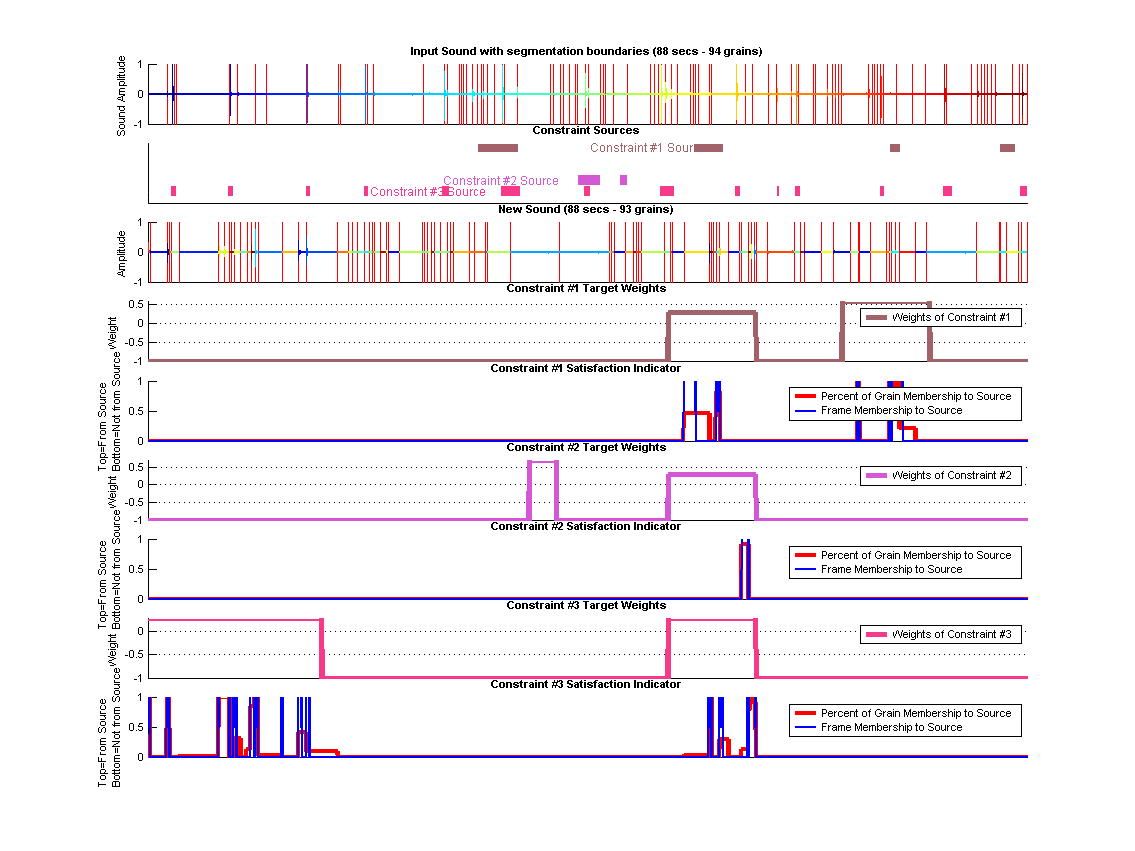
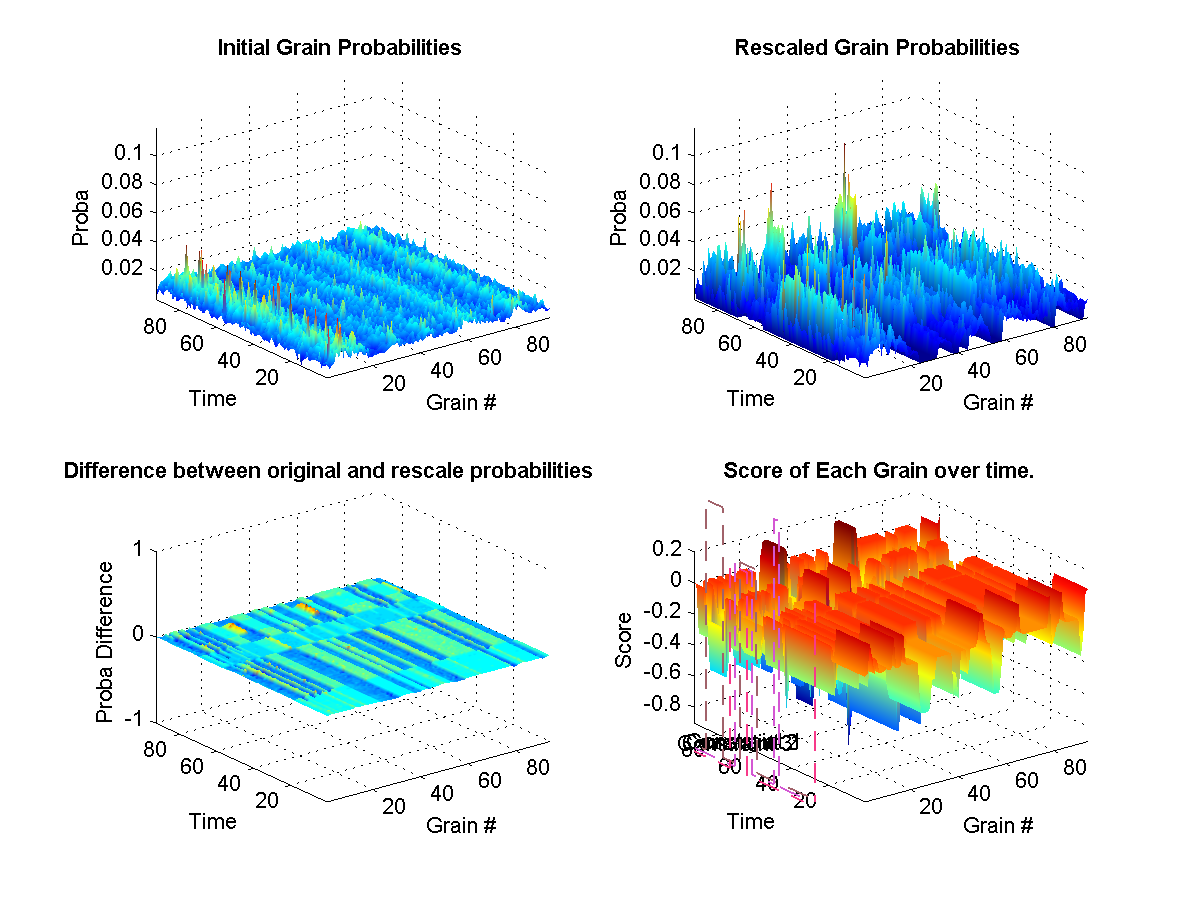
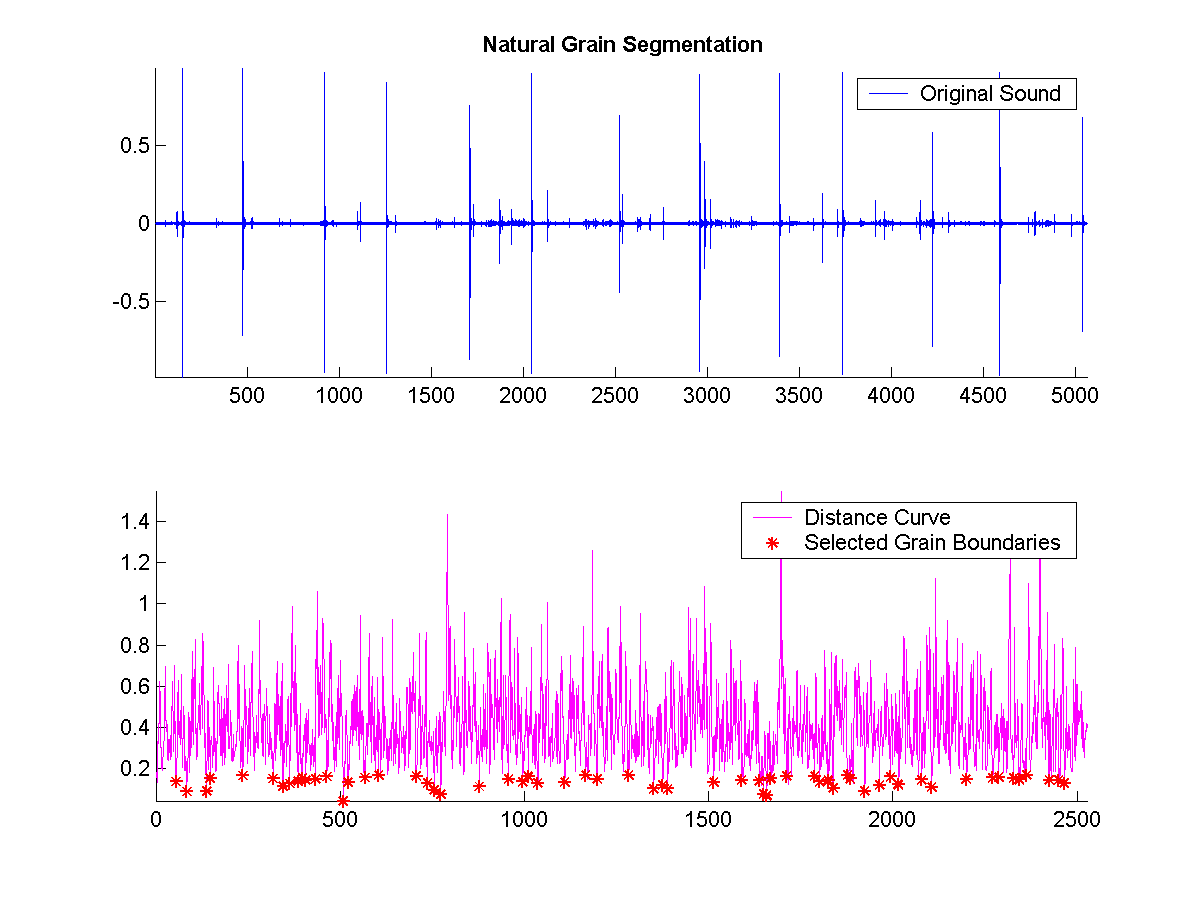
Natural-Grain Synthesis
|
Segmented Original Sound
New Sound
|
Wavelet Synthesis
|
New Sound